Directional Boring vs. Trenching: Which Method is Right for Your Project?
- Grid Tech
- Jun 13, 2023
- 3 min read
In the domain of underground utility installation, two most prominent methods vie for supremacy: trenching and directional boring. Understanding the differences and benefits of each approach empowers project managers, construction professionals and property owners to make the best decision.
Today, in this blog post we are going to talk about the distinct characteristics, advantages and considerations of directional boring and trenching. The detailed knowledge helps you to choose the method perfectly align with your project objectives, budget and environmental impact.

What are Trenching?
Trenching is one of the most traditional processes of underground utility installation. This involves excavating a trench along the desired path for wire and other utility installation requirements. It is often used when the terrain is suitable for open excavation and when deep trenches are necessary.
Key Benefits of Trenching:
Cost-Effectiveness: Trenching is generally more cost-effective option for shorter distances and shallow installation. It requires less specialized equipment and can be easily completed with available standard excavation machinery.
Easy Access for Maintenance and Repairs: Trenching provides easier access for maintenance and repairs since utilities are exposed and readily accessible within the trench. This can save you time and effort in the long run.
What is Directional Boring?
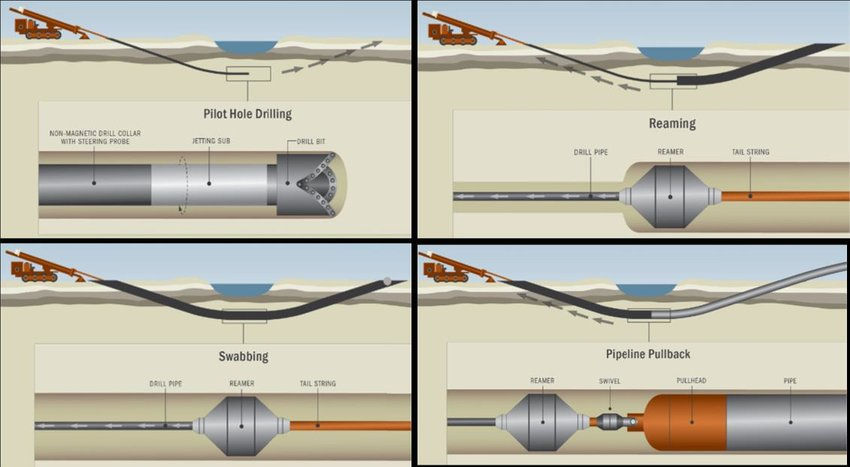
Direction Boring process is also known as Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD). This is a great method, widely used to install underground utilities without the need for extensive excavation. It involves drilling a small pilot hole and then enlarging it to the desired size using specialized equipment and machinery. This technique allows for the installation of utilities beneath roads, landscapes, rivers and other obstacles.

Key Advantages of Direction Boring Technique:
Minimal Surface Disruption: One of the key advantages of directional boring is its ability to minimize surface disruption. Unlike trenching, direction boring needs only small entry and exit points, reducing damage to existing infrastructure and minimizing the need for restoration.
Versatility: Directional boring can be used in a variety of soil conditions, including hard rock, clay and sandy soils. It offers flexibility in navigating obstacles, such as existing utilities, structures, and environmentally sensitive areas.
Factor to Consider When Choosing Between Trenching and Directional Boring
When deciding between trenching and directional boring for your project, several key factors should be considered. Evaluating these factors will help you determine the most suitable method for your specific utility installing needs. Here we explore some factors to consider:
Project Scope:
Assess the length and depth of the utility installation required for your project. Directional boring is typically more suitable for longer distances and deeper installations, as it allows for the drilling of horizontal bores over extended lengths. On the other hand, trenching is often preferred for shorter distances or shallower installations.
Ground Conditions:
Consider the soil composition and terrain of your project site. Directional boring is well-suited for challenging terrains such as rocky or hard soil conditions, as it can easily navigate obstacles and drill through various soil types. On this context, trenching is generally more feasible in areas with softer soil that can be easily excavated.
Environmental Impact:
Assess the impact on the environment and existing infrastructure. Compared to trenching, directional boring tends to have a lower environmental impact since it minimizes surface disruption and requires less restoration. If your project site is located in an environmentally sensitive area or requires minimal disturbance, directional boring may be the most preferred choice for your project.

Cost Considerations:
Evaluate your budget and cost constraints before choosing between directional boring and trenching for your project. Directional boring often requires specialized equipment, skilled operators, and advanced drilling techniques. All these can make the process more expensive option.
On the other hand, trenching can be more cost-effective for shorter distances and shallower installations since it involves less specialized equipment and can be completed with standard excavation machinery.
Regulatory Requirements: Be aware of any specific regulations or permits that may apply to your project. Some regions or municipalities may have specific guidelines or restrictions regarding the use of trenching or directional boring methods for utility installations. So, before making your final decision, always ensure that you comply with all applicable regulations.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Project
In order to determine the most suitable method for your project, carefully evaluate the aforementioned factors. If your project requires minimal surface disruption, traverses challenging terrain, or prioritizes environmental impact, directional boring may be the preferred choice. On the other hand, if your project has a smaller scope, requires easier access for maintenance and repairs, or is cost-sensitive, trenching may be more appropriate.

Comments