Underground Boring Services: Revolutionizing Construction and Infrastructure Development
- Grid Tech
- May 23, 2023
- 4 min read
Introduction
In the realm of construction and infrastructure development, efficiency, precision, and sustainability are paramount. One groundbreaking solution that has emerged to meet these demands is underground boring services. This innovative method revolutionizes the traditional approach to construction, allowing for the installation of utilities, pipelines, and other infrastructure beneath the ground without disruptive excavation. In this article, we will delve into the world of underground boring services, exploring its benefits, applications, and the significant impact it has on modern construction projects.
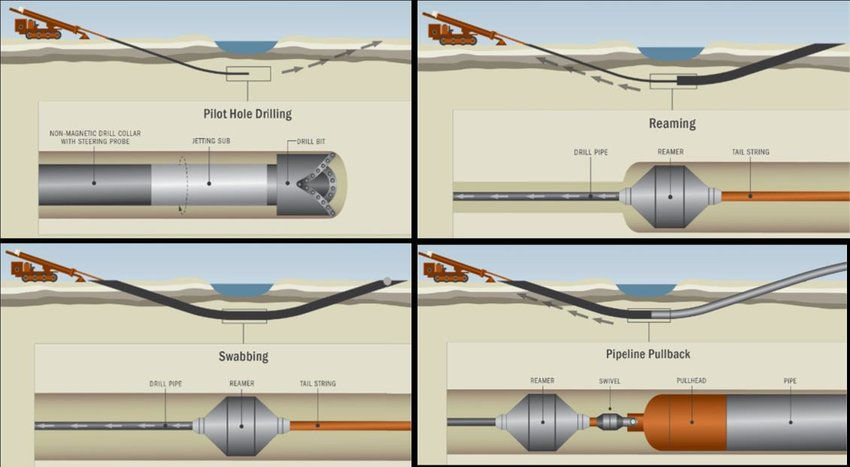
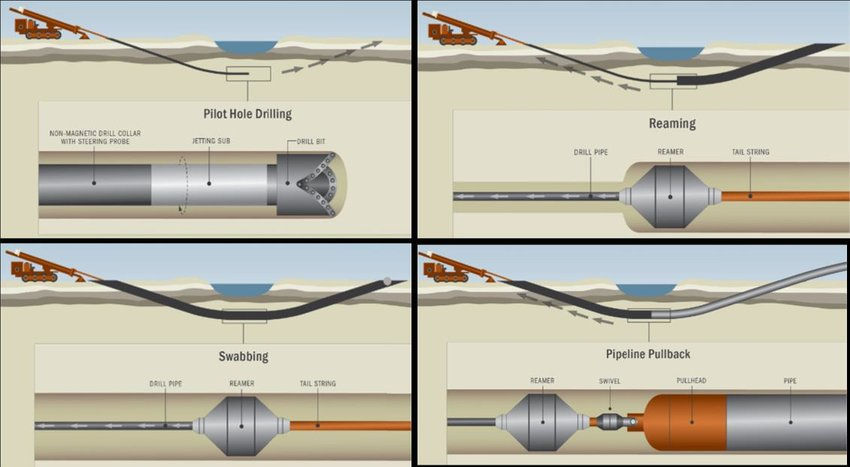
The Rise of Underground Boring Services:
The traditional method of trenching for the installation of utilities and infrastructure often entails significant disruptions, such as road closures, disruption to local communities, and environmental damage. However, underground boring services offer a more efficient and sustainable alternative. By utilizing advanced drilling techniques, boring services enable the creation of tunnels and conduits beneath the surface, minimizing surface disruptions while maximizing productivity.
The Benefits of Underground Boring Services
2.1 Precision and Efficiency:
Underground boring services allow for precise drilling, ensuring accurate alignment and installation of utilities. This level of precision significantly reduces the chances of damage or errors during construction, saving both time and money. Furthermore, boring services expedite project timelines by minimizing the need for extensive excavation, resulting in faster project completion.
2.2 Minimized Disruption:
One of the most significant advantages of underground boring services is the minimal disruption caused to the surrounding environment and communities. Unlike traditional trenching, which often requires road closures and other inconveniences, boring services can be performed without disturbing surface activities. This reduces the impact on daily routines, lessens traffic congestion, and enhances public safety.
2.3 Environmental Preservation:
Underground boring services contribute to environmental preservation by minimizing soil excavation and disturbance. This approach prevents soil erosion, preserves natural habitats, and helps maintain the ecological balance. Additionally, by reducing the need for extensive excavation, carbon emissions from heavy machinery and transportation are significantly reduced.
Applications of Underground Boring
3.1 Utility Installations:
Underground boring services are widely used for the installation of utilities, such as water and sewage pipelines, fiber optic cables, gas lines, and electrical conduits. The precise drilling techniques ensure accurate alignment, allowing for efficient and reliable utility networks.

3.2 Transportation Infrastructure:
Boring services play a vital role in the construction and expansion of transportation infrastructure. They enable the installation of underground tunnels for roads, railways, and pedestrian walkways. By avoiding surface disruptions, traffic congestion is minimized, and the overall transportation system is optimized.
3.3 Urban Development:
In urban areas, where space is often limited, underground boring services provide a solution for expanding infrastructure without encroaching on valuable surface space. Boring tunnels can accommodate utilities, parking structures, and even commercial spaces, maximizing land usage and preserving the aesthetic appeal of cities.
Advancements in Underground Boring Technology:
Over the years, underground boring technology has witnessed significant advancements, further enhancing its capabilities and expanding its applications. Here are some notable innovations driving the evolution of underground boring services:
4.1 Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD):
Horizontal Directional Drilling is a technique that allows for the installation of underground utilities by drilling horizontally from a starting point to a designated endpoint. This method is particularly useful when obstacles, such as rivers or densely populated areas, need to be bypassed. HDD minimizes surface disruptions and reduces the environmental impact while providing precise and efficient utility installations.
4.2 Microtunneling:
Microtunneling involves the use of remotely operated microtunnel boring machines (MTBMs) to create tunnels for utilities installation. These machines can excavate tunnels with diameters as small as a few feet, making them ideal for projects that require minimal surface disruption. Microtunneling provides precise control, ensuring accurate alignment and efficient installation of pipelines and conduits.
4.3 Auger Boring:
Auger boring employs a rotating cutting head, known as an auger, to excavate soil and create tunnels for utility installation. This method is commonly used for projects that require longer and larger-diameter tunnels. Auger boring offers versatility, enabling the installation of utilities at varying depths and distances.
Safety Considerations and Regulations:
Safety is of paramount importance in underground boring services. Due to the nature of working underground, there are specific safety considerations and regulations that must be followed to mitigate risks. These include:
5.1 Proper Training and Equipment:
Operators and workers involved in underground boring services should undergo comprehensive training to ensure they possess the necessary skills and knowledge. Additionally, using state-of-the-art equipment and technology enhances safety and productivity during the boring process.
5.2 Utility Locating and Damage Prevention:
Accurate utility locating is crucial to prevent accidental damage to existing infrastructure during the boring process. Advanced detection methods, such as ground-penetrating radar and electromagnetic locators, are utilized to identify and mark the location of buried utilities.
5.3 Compliance with Environmental Regulations:
Underground boring services must comply with environmental regulations to protect ecosystems and prevent pollution. Proper waste management, soil erosion control measures, and adherence to noise and vibration limits are essential to minimize environmental impact.

Conclusion:
Underground boring services have emerged as a game-changer in construction and infrastructure development. With their precision, efficiency, and minimal surface disruption, these services are revolutionizing the industry. As technology continues to advance and safety measures improve, the future of underground boring services holds immense potential. By embracing these innovative techniques, we can create a more sustainable and efficient built environment while minimizing the impact on communities and the environment. The continued evolution of underground boring services will shape the way we construct, expand, and maintain infrastructure, leading us toward a more advanced and sustainable future.

Comments